HIPAC COMPACTION TECHNIQUE
WDI’s strand compaction technique HiPac sets the standards for gentle yet highly effective compaction of strands. Constant research on the parameters of strand compaction have led to the development of WDI’s
HiPac compaction technique. HiPac compromises for highest compaction grades on one hand and most gentle treatment of the wire’s metal structure on the other hand. As a result, HiPac compaction provides highest breaking forces with least possible impact on bending fatigue, adding several benefits to PYTHON wire rope:
Less wear and tear
The increased contact area to drum and sheaves of the compacted strand significantly reduces wear in comparison to the uncompacted strand. While the uncompacted strand has a punctual contact to the sheave, the contact area of the compacted strand is much higher. This results in reduced wear and tear and increased service life of both rope and system components.
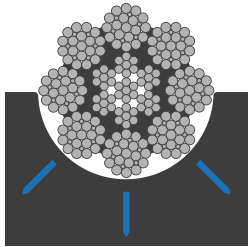
high contact point bearing pressure
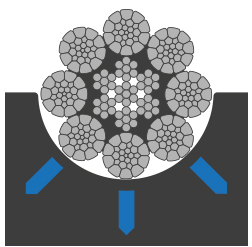
reduced bearing pressure
Multi-layer drums
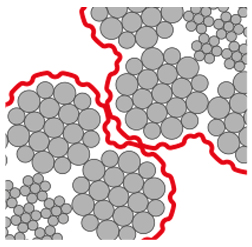
In multi layer systems, uncompacted wire rope causes interlocking of wires of two neighbouring wraps in the crossover zones on the drum. Interlocking is often accompanied by audible crackling and in severe cases, flying sparks can be observed. This leads to accelerated failure of the outer wires, reason for early discard of the rope.
HiPac compaction gives our ropes a smooth surface of each strand. Interlocking and hence the destruction of the outer wires is reduced effectively, elevating the rope’s service life to a more economic level.
Proper spooling pattern
The rope’s low tendencies to ovalisation and diameter reduction in service provide a very uniform spooling pattern, the most important requirement for Lebus multi layer systems to work correctly. HiPac enabled PYTHON ropes have proven to spool properly even with a high number of layers.